Project management is a multi-disciplinary field that requires careful planning, resource allocation, risk management, and performance tracking. Many project managers rely on experience and intuition to guide their projects. However, mathematical algorithms provide a systematic and data-driven approach. This approach can help optimize project outcomes. These algorithms are particularly useful in complex IT implementation projects and construction projects. They are useful in any other initiatives requiring efficient coordination of tasks and resources.
In this article, we will explore some of the key mathematical algorithms. These algorithms can be applied to project management processes. We will break down how they work and why they are valuable.
1. Critical Path Method (CPM)
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is one of the most widely used algorithms for project scheduling. It helps project managers find the sequence of tasks. These tasks must be completed on time to avoid delays in the overall project. By focusing on the “critical path,” you can allocate resources more effectively and identify potential bottlenecks early.
Key Components:
- Tasks: Individual units of work in a project.
- Dependencies: Relationships between tasks, indicating which tasks must be completed before others can begin.
- Duration: Time required to complete each task.
- Critical Path: The longest sequence of dependent tasks.
How it works:
- Break the project into individual tasks.
- Identify dependencies between tasks.
- Estimate the duration of each task.
- Calculate the earliest and latest possible start and finish times for each task.
- Identify the critical path by finding the longest path through the project schedule.
Example Diagram:
Below is a simplified network diagram for CPM, where Task A, B, and C are critical path tasks.

2. Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
The Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) is used to manage projects where task durations are uncertain. It helps project managers estimate the likelihood of completing a project within a specified time frame. They consider optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely task durations.
Formula:
PERT uses a weighted average formula to estimate task durations:
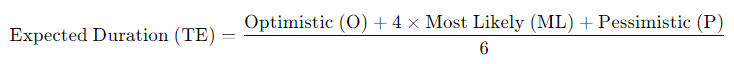
How it works:
- Assign optimistic (O), most likely (ML), and pessimistic (P) durations to each task.
- Use the PERT formula to calculate the expected time for each task.
- Create a project network diagram similar to CPM, incorporating the calculated durations.
- Analyze the network to determine the expected project completion time and possible delays.
Example Diagram:
Below is a PERT chart with multiple task time estimates.
3. Monte Carlo Simulation
Monte Carlo Simulation is a probabilistic technique used to understand the impact of risk and uncertainty in project scheduling and cost management. It uses random sampling to calculate various possible outcomes of a project, providing a statistical distribution of potential results.
How it works:
- Define the possible ranges of project variables (e.g., task duration, costs).
- Run a large number of simulations, each time randomly selecting values for these variables.
- Analyze the outcomes to understand the probability of meeting certain deadlines or budgets.
Benefits:
- Provides a visual representation of potential project outcomes.
- Helps in risk management by identifying probabilities of delays or budget overruns.
Example Graph:
The graph below shows the probability distribution of project completion times using Monte Carlo simulation.
4. Linear Programming (LP) for Resource Allocation
Linear Programming (LP) is an optimization algorithm that helps allocate limited resources to competing tasks or objectives, minimizing costs or maximizing productivity. This is particularly useful for managing project budgets and assigning resources in the most efficient way.
LP Formula:
Maximize or minimize a linear objective function:

How it works:
- Define the objective function (e.g., minimize project cost).
- Identify the constraints (e.g., budget limits, resource availability).
- Use LP solvers or algorithms to find the optimal solution for resource allocation.
Example Diagram:
Below is an example of a linear programming graph where the optimal solution is found at the intersection of constraints.
5. Earned Value Management (EVM)
Earned Value Management (EVM) is a performance measurement algorithm that helps track project progress and forecast future performance. It compares the planned progress with actual progress to assess how well the project is adhering to schedule and budget.
Key Metrics:
- Planned Value (PV): The estimated cost of work planned to be completed by a certain date.
- Earned Value (EV): The value of work actually performed by the same date.
- Actual Cost (AC): The actual cost incurred by the same date.
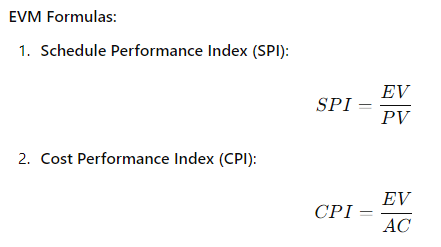
How it works:
- Calculate PV, EV, and AC at a given point in the project.
- Use SPI and CPI to determine if the project is on track, behind schedule, or over budget.
6. Heuristic Algorithms for Task Scheduling
Heuristic algorithms, such as Genetic Algorithms or Simulated Annealing, can be applied to optimize task scheduling in complex projects. These algorithms use an iterative approach to explore possible solutions. They aim to find the best possible schedule while adhering to constraints.
Benefits:
- Heuristic algorithms are useful for large-scale projects with multiple inter-dependencies.
- They provide near-optimal solutions when exact methods are computationally impractical.
How it works:
- Define the task scheduling problem with constraints (e.g., deadlines, resource limits).
- Use a heuristic algorithm to generate an initial solution.
- Iteratively refine the solution through mutations or adjustments until an optimal or near-optimal solution is found.
Conclusion
Mathematical algorithms provide powerful tools for optimizing project management processes. Project managers use algorithms from scheduling tasks with CPM and PERT. They manage risks with Monte Carlo simulation. Additionally, they optimize resources with linear programming. These algorithms enable project managers to make data-driven decisions. They also improve efficiency and mitigate risks. Incorporating these algorithms into your project management toolkit can help ensure successful project outcomes, even in complex and uncertain environments.
By understanding and applying these techniques, project managers can achieve better control over timelines, resources, and costs. This ultimately leads to more predictable and successful project deliveries.
Feel free to adapt this article according to your specific needs! For images, diagrams, and charts mentioned in the article, I can generate custom visual content if you’d like.


Leave a comment